ML-Based Optimization of Large-Scale Systems for 5G/6G Networks and Smart Microgrid
This project aims to develop state-of-the-art ML techniques to improve the performance of large-scale systems. As case studies, we focus on microgrid energy management and 5G/6G radio access network (RAN) management. In particular, it involves the following topics:
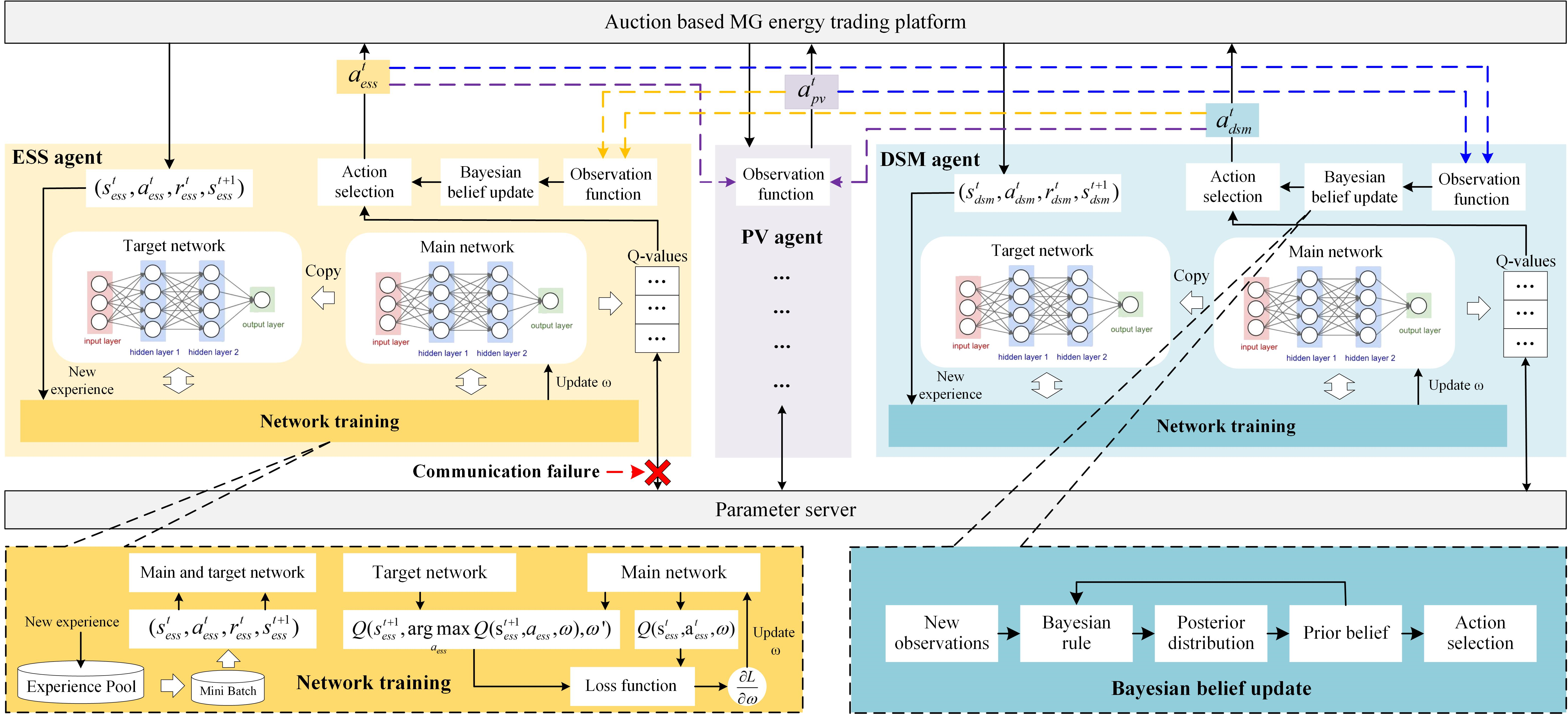
Multi-agent reinforcement learning: Microgrids (MGs) are important players for the future transactive energy systems in the smart grid. Although there have been many works on MG energy management, most studies assume a perfect communication environment, where communication failures are not considered. In this paper, we consider the MG as a multiagent environment with IoT devices in which AI agents exchange information with their peers for collaboration. However, the collaboration information may be lost due to communication failures or packet loss. Such events may affect the operation of the whole MG. To this end, we propose a multi-agent Bayesian deep reinforcement learning (BA-DRL) method for MG energy management under communication failures. We first define a multi-agent partially observable Markov decision process (MAPOMDP) to describe agents under communication failures, in which each agent can update its beliefs on the actions of its peers. Then, we apply a double deep Q-learning (DDQN) architecture for Q-value estimation in BA-DRL, and propose a belief-based correlated equilibrium for the joint-action selection of multiagent BA-DRL. Finally, the simulation results show that BA-DRL is robust to both power supply uncertainty and communication failure uncertainty. BA-DRL has 4.1% and 10.3% higher reward than Nash Deep Q-learning (Nash-DQN) and alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) respectively under 1% communication failure probability.
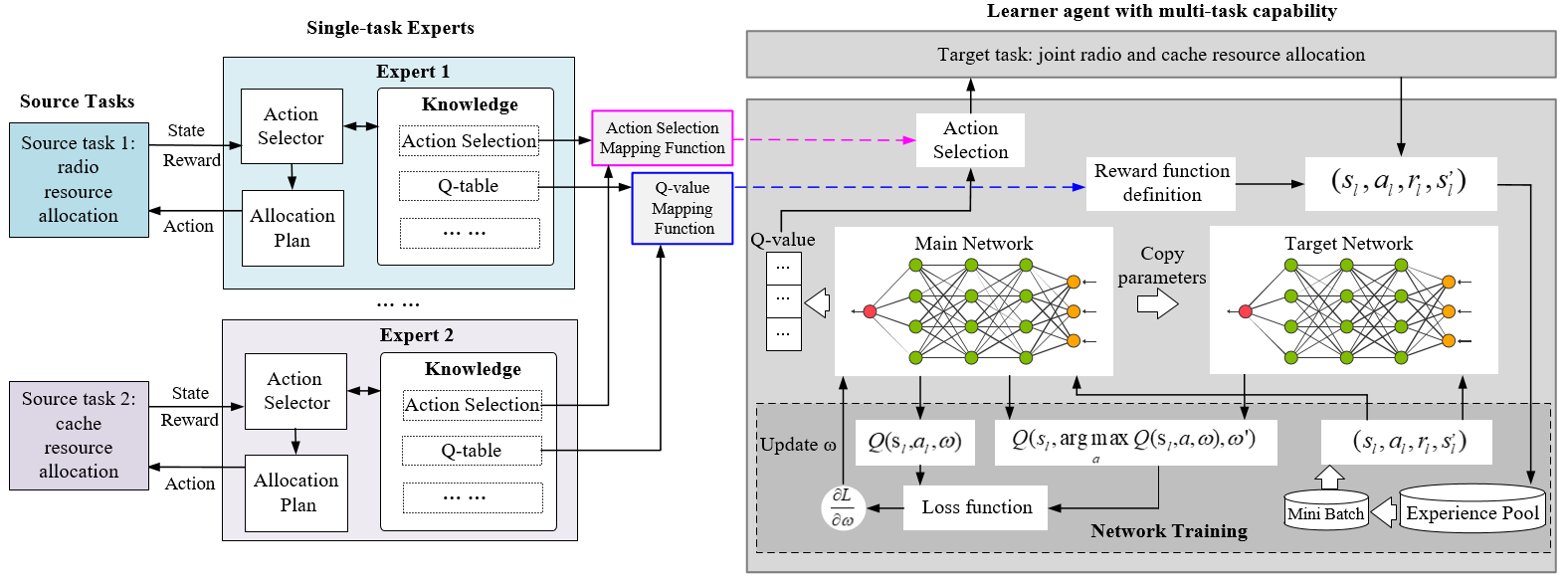
Deep Transfer Reinforcement Learning: Network slicing is a critical technique for 5G communications that covers radio access network (RAN), edge, transport and core slicing. The evolving network architecture requires the orchestration of multiple network resources such as radio and cache resources. In recent years, machine learning (ML) techniques have been widely applied for network management . However, most existing works do not take advantage of the knowledge transfer capability in ML. In this paper, we propose a deep transfer reinforcement learning (DTRL) scheme for joint radio and cache resource allocation to serve 5G RAN slicing. We first define a hierarchical architecture for joint resourc e allocation. Then we propose two DTRL algorithms: Q-valuebased deep transfer reinforcement learning (QDTRL) and action selection-based deep transfer reinforcement learning (ADTRL). In the proposed schemes, learner agents utilize expert agents’ knowledge to improve their performance on current tasks. Th e proposed algorithms are compared with both the model-free exploration bonus deep Q-learning (EB-DQN) and the modelbased priority proportional fairness and time-to-live (PPF-TTL) algorithms. Compared with EB-DQN, our proposed DTRLbased method presents 21.4% lower delay for Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC) slice and 22.4% higher throughput for enhanced Mobile Broad Band (eMBB) slice, while achieving significantly faster convergence than EB-DQN. Moreover, 40.8% lower URLLC delay and 59.8% higher eMBB throughput are observed with respect to PPF-TTL.
Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning: Energy efficiency (EE) is one of the most important metrics for envisioned 6G networks, and sleep control, as a cost-efficient approach, can significantly lower power consumption by switching off network devices selectively. Meanwhile, the reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) has emerged as a promising technique to enhance the EE of future wireless networks. In this work, we jointly consider sleep and transmission power control for RIS-aided energy-efficient networks. In particular, considering the timescale difference between sleep control and power control, we introduce a cooperative hierarchical deep reinforcement learning (Co-HDRL) algorithm, enabling hierarchical and intelligent decision-making. Specifically, the meta-controller in Co-HDRL uses cross-entropy metrics to evaluate the policy stability of sub-controllers, and sub-controllers apply the correlated equilibrium to select optimal joint actions. Compared with conventional HDRL, Co-HDRL enables more stable high-level policy generations and low-level action selections. Then, we introduce a fractional programming method for RIS phase-shift control, maximizing the sum-rate under a given transmission power. In addition, we proposed a low-complexity surrogate optimization method as a baseline for RIS control. Finally, simulations show that the RIS-assisted sleep control can achieve more than 16% lower energy consumption and 30% higher EE than baseline algorithms.
The related publications include the following, and all publications can be download in my Google Scholar
H. Zhou, M. Erol-Kantarci, Y. Liu, and H. V. Poor, “A Survey on Model-based, Heuristic, and Machine Learning Optimization Approaches in RIS-aided Wireless Networks,” IEEE Communications Survey & Tutorials, vol.26, no.2, pp.781-823, 2nd quarter, 2024.
H. Zhou, M. Erol-Kantarci, Y. Liu, and H. V. Poor, “Heuristic Algorithms for RIS-assisted Wireless Networks: Exploring Heuristic-aided Machine Learning,” IEEE Wireless Communications, vol.3, no.4, pp.1-9, Aug. 2024.
H. Zhou, M. Elsayed, M. Bavand, R. Gaigalas, S. Furr, and M. Erol-Kantarci, “Cooperative Hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning based Joint Sleep, Power, and RIS Control for Energy-Efficient RAN,” IEEE Trans. on Cognitive Communications and Networking, pp.1-15, Jul. 2024.
H. Zhang, H. Zhou, M. Elsayed, M. Bavand, R. Gaigalas, Y. Ozcan, and M. Erol-Kantarci, “On-Device Intelligence for 5G RAN: Knowledge Transfer and Federated Learning enabled UE-Centric Traffic Steering,” IEEE Trans. on Cognitive Communications and Networking, vol.10, no.2, pp. 689-705, Apr. 2023.
M. Razghandi, H. Zhou, M. Erol-Kantarci, and D. Turgut, “Smart Home Energy Management: VAE-GAN synthetic dataset generator and Q-learning,” IEEE Trans. on Smart Grid, vo.15, no.2, pp.1562-1573, May 2024.
H. Zhou, M. Erol-Kantarci, and H. V. Poor, “Knowledge Transfer and Reuse: A Case Study of AI-enabled Resource Management in RAN Slicing,” IEEE Wireless Communications, vol.30, no.5, pp.1-10, Oct. 2023.
H. Zhou, M. Erol-Kantarci, and H. V. Poor, “Learning from Peers: Deep Transfer Reinforcement Learning for Joint Radio and Cache Resource Allocation in 5G Network Slicing,” IEEE Trans. on Cognitive Communications and Networking, vol.8, no.4, pp.1925-1941, Dec.2022.
H. Zhou, A. Aral, I. Brandic, and M. Erol-Kantarci, “Multi-agent Bayesian Deep Reinforcement Learning for Microgrid Energy Management under Communication Failures,” IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol.9, no.14, pp.11685-11698, Jul. 2022.
