Large Language Model-driven Efficient and Flexible NextG Cellular Network Management
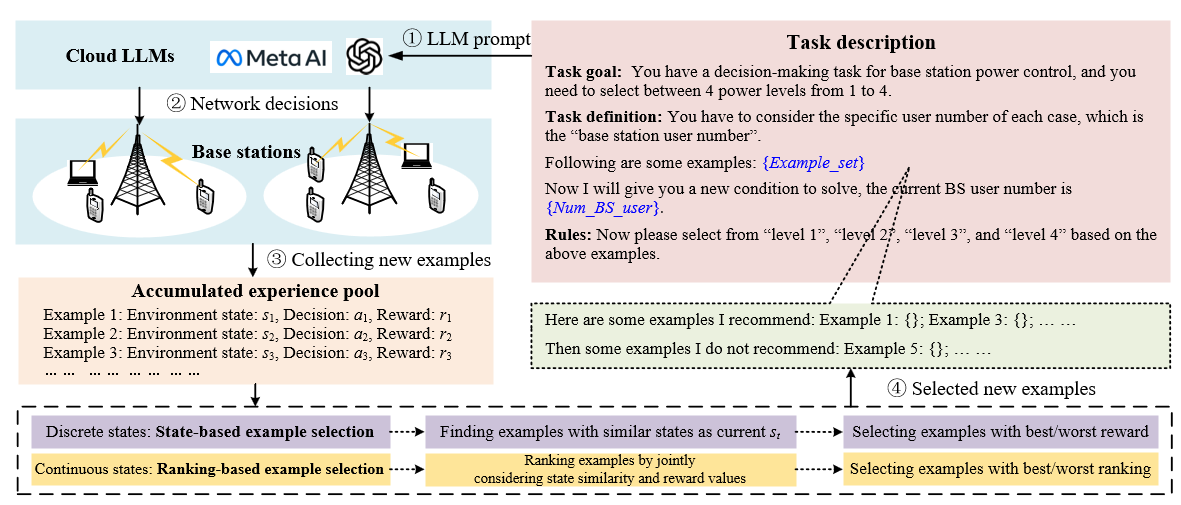
I am a team leader for this project and supervise 3 PhD students. It aims to investigate how state-of-the-art large language model (LLM) techniques can be used for efficient and flexible nextG wireless networks. As the main proposal writer, this collaboration has been granted the Samsung Global Research Outreach (GRO) program (150,000 USD for 1 year, and only 11 projects are selected worldwide).
Specifically, it aims to utilize LLMs to develop a series of solutions for the network management of next-generation communication networks, addressing the following challenges:
How to flexibly deploy LLMs in cellular networks? Proper deployment strategies are the prerequisite for applying LLMs to cellular networks. With billions of parameters, LLMs require considerable storage and computational resources for implementation. However, network devices usually have limited computational capabilities.
How to build a telecom-specific LLM? A telecom-specific LLM indicates great benefits for cellular network management, e.g., answering network-related questions, summarizing existing techniques and providing trouble-shooting suggestions. However, there are several obstacles, such as dataset scarcity and privacy issues, complicated networking concepts, computation resources costs, etc.
How to use LLMs efficiently for cellular network management? LLMs can be used in various approaches, e.g., pre-training, fine-tuning, or prompting. Identifying the most efficient approach to LLM usage is crucial to handle diverse network management tasks.
To this end, we have proposed multiple solutions, which can be found in the following publications. All publications can be download in my Google Scholar
H. Zhou, C. Hu, Y. Yuan, Y. Cui, Y. Jin, C. Chen, H. Wu, D. Yuan, L. Jiang, D. Wu, X. Liu, C. Zhang, X. Wang, and J. Liu, “Large Language Model (LLM) for Telecommunications: A Comprehensive Survey on Principles, Key Techniques, and Opportunities,” IEEE Communications Survey & Tutorials, pp.1-52, Sep. 2024.
H. Zhou, C. Hu, D. Yuan, Y. Yuan, D. Wu, X. Chen, H. Tabassum, X. Liu, “Large Language Models (LLMs) for Wireless Networks: An Overview from the Prompt Engineering Perspective,” IEEE Wireless Communications, pp.1-10, Jan. 2025.
H. Zhou, C. Hu, D. Yuan, Y. Yuan, D. Wu, X. Liu, Z. Han, and C. Zhang, “Generative AI as a Service in 6G Edge-Cloud: Generation Task Offloading by In-context Learning,” IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, pp.1-5, Dec. 2024.
H. Zhou, C. Hu, D. Yuan, Y. Yuan, D. Wu, X. Liu, and C. Zhang, “Large Language Model (LLM)-enabled In-context Learning for Wireless Network Optimization: A Case Study of Power Control,” arXiv:2408.00214, pp.1-5, Aug. 2024.
Z. Yan, H. Zhou, H. Tabassum, and X. Liu, “Hybrid LLM-DDQN based Joint Optimization of V2I Communication and Autonomous Driving,” arXiv:2410.08854, pp.1-5, Oct. 2024.
C. Hu, H. Zhou, D. Wu, X. Chen, J. Yan, and X. Liu, “Self-Refined Generative Foundation Models for Wireless Traffic Prediction,” arXiv:2408.10390, pp.1-5, Aug. 2024.
